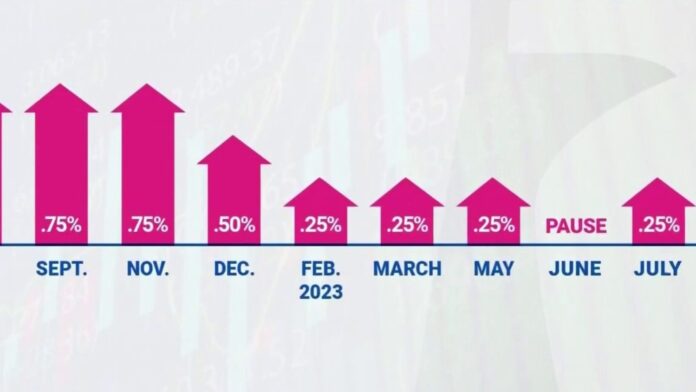
The US central bank has implemented the highest interest rates in 22 years in an effort to stabilise the world’s largest economy and curb rising prices. This decision resulted in the Federal Reserve’s influential benchmark rate being raised to a range of 5.25% to 5.5%, marking the eleventh increase since early 2022, when the Fed began raising borrowing costs to combat economic overheating and inflation.
Despite this rate hike, the Fed did not provide clear indications of its future actions. Concurrently, central bank meetings in Europe and Japan were impending, with the Bank of England expected to raise its key rate from 5% at its upcoming meeting due to the UK’s 7.9% inflation.
Some analysts believe that the Fed’s actions have been sufficient, as inflation in the US has decreased to 3% in June from its peak of over 9% last year. This downward trend, combined with the restrictive Fed funds rate, is seen as a potential measure to slow down economic activity and allow inflation to subside. As a result, further rate hikes in the US are not anticipated for the rest of the year.
The Fed’s recent interest rate increases have transitioned the economy away from near-zero rates, which were implemented during the financial crisis. These moves have impacted the public, resulting in higher costs for loans related to housing, business expansion, and other activities. The aim is to reduce borrowing demand and encourage saving, ultimately cooling the economy and curbing price hikes.
However, the US economy has demonstrated resilience, especially in the labour market, with consistent job additions and rising wages. The Fed acknowledges the progress made, but core inflation (excluding food and energy prices) remains more than double the Fed’s 2% inflation target.
The central bank is cautious about prematurely declaring victory over inflation, as historical mistakes in the 1960s and 1970s have shown that easing inflation can reignite if not managed carefully. Therefore, the Fed remains vigilant in its efforts to balance economic stability and price control.